The Authorization Code Grant is usually used to delegate authorization from one web application to another.
The OAuth 2.0 RFC depicts the Authorization Code Grant as follows:
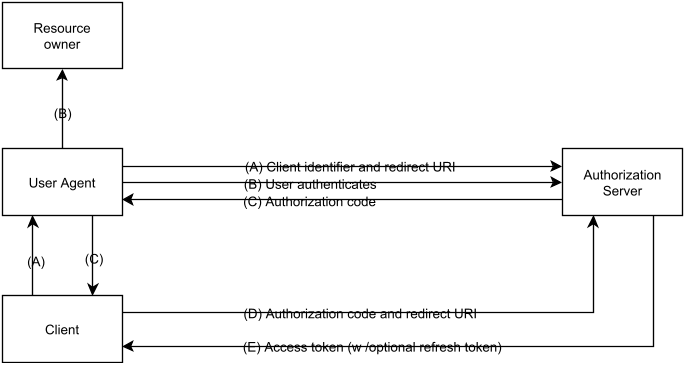
We give an example to illustrate this grant type.
- Goal:
Delegate authorization to access Facebook (Authorization Server) pictures to Pinterest (Client).
- The user (Resource Owner) navigates in her browser (User-Agent) to Pinterest (Client). Pinterest would like to display pictures contained in the user's Facebook account.
- (A) Pinterest redirects the user to Facebook (Authorization Server), with a request saying that Pinterest (client_id) would like to access the user's pictures (scope).
- (B) The user authenticates with Facebook and is asked if she would like to grant Pinterest access to her pictures. We assume the user grants access.
- (C) Facebook sends a redirect containing an Authorization Code to Pinterest.
- (D) Pinterest directly authenticates with Facebook and then uses the Authorization Code to obtain an Access Token (E).
- Finally, Pinterest uses the Access Token to access the user's Facebook pictures.
