Submenu – JWKS Providers
JWK is a JSON representation of cryptographic keys widely used in the context of JWT. A set of such keys is known as JWKS, a JSON Web Key Set. JWKS is also the format used by the gateway to configure verification of access tokens.
When a JSON Web Key Set provider is configured to be used in a mapping, the keys in the set will be consulted when trying to verify a JWS or when decrypting a JWE.
The gateway uses a 2-stage filtering process to reduce the number of processed keys:
- Stage 1 – JWKS are filtered by their Issuer information.
- Stage 2 – The individual keys of the selected JWKS are finally filtered according to their key properties.
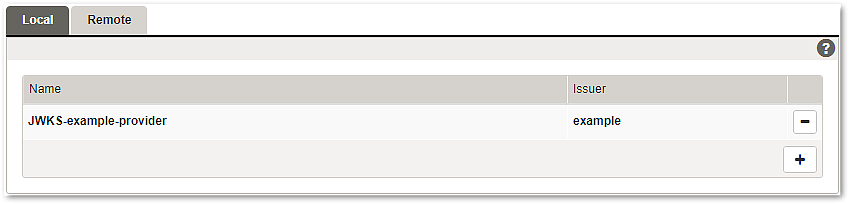
Local JWKS
Local (static) JWKS can be managed in the Local tab:
Name | When adding a new JWKS you should choose and add a unique provider name here. This provider name will appear in a drop-down list when choosing a JWKS provider for a mapping. |
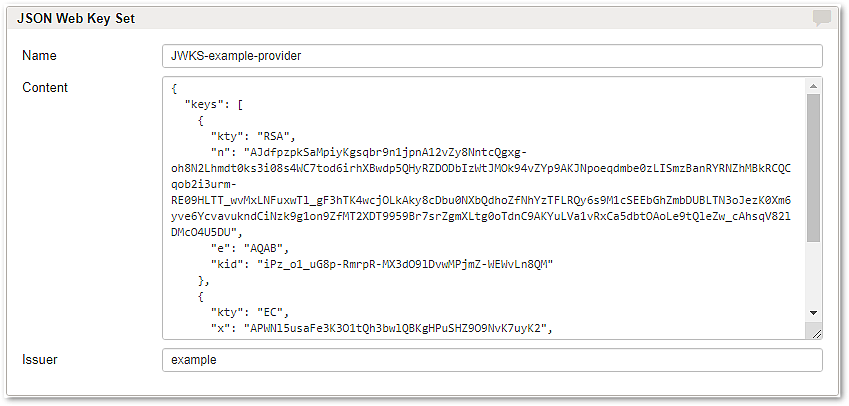
Content | This field holds the JWKS with its individual keys. Simply copy the JWKS content into the text box. |
Issuer | This information is used for the first stage of the JWKS filter process. The issuer information is optional. |
JWKS without issuer information is less restricted and do potentially matches more often. This can result in a higher number of processed keys.
A fully configured local JWKS may look like the following:
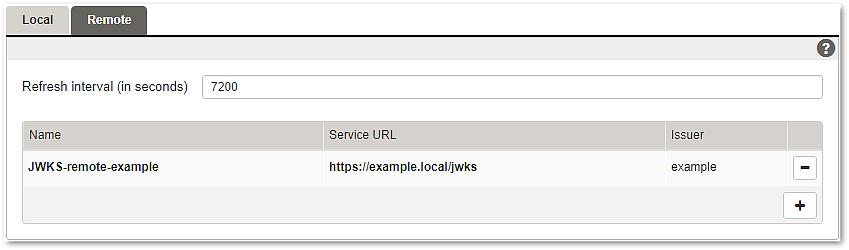
Remote JWKS
When adding a new Remote JWKS Provider configuring settings on the Basic and additional SSL settings are necessary. For security reasons any remote source normally requires a secured connection using hostname verification and a valid SSL certificate/CA chain that can be configured in the SSL tab.
Refresh interval (in seconds) | Here you can choose the polling interval for re-fetching remotely stored JWKS from the Service URL addresses.
|
Name | When adding a new JWKS you should choose and add a unique provider name here. This provider name will appear in a drop-down list when choosing a JWKS for a mapping. |
Service URL | This field holds the URL from where the JWKS can be fetched. It is the source URL of the key set. |
Issuer | This information is used for the first stage of the JWKS filter process. The issuer information is optional. |
JWKS without issuer information are less restricted and do potentially match more often. This can result in a higher number of processed keys.
Tab – Basic
When adding a new Remote JWKS Provider configuring settings on the Basic and additional SSL settings are necessary.
Name | When adding a new JWKS you should choose and add a unique provider name here. This provider name will appear in a drop-down list when choosing a JWKS for a mapping. |
Service URL | This field holds the URL from where the JWKS can be fetched. It is the source URL of the key set. |
Issuer | This information is used for the first stage of the JWKS filter process. The issuer information is optional. |
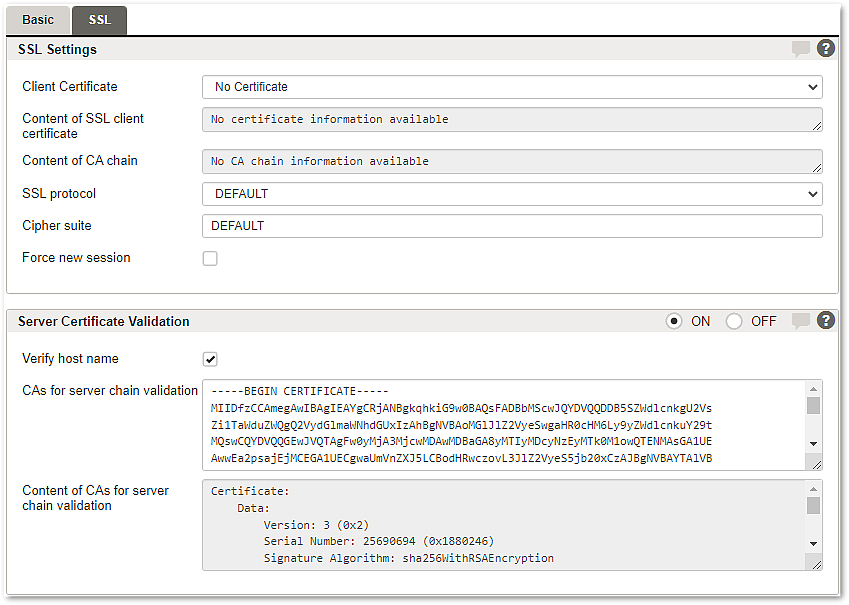
Tab – SSL
For security reasons any remote source normally requires a secured connection using hostname verification and a valid SSL certificate/CA chain that can be configured in the SSL tab.
Section SSL Settings | |
Client certificate | A selectable list of SSL/TLS certificates for this client. |
Content of SSL client certificate | Shows the content of the certificate. |
Content of CA chain | Shows the chain of trust of the certificate chain. |
SSL protocol | The SSL/TLS version which will be used by this back-end can be set here. If the setting is left empty, Airlock Gateway defaults will be used. |
Cipher suite | List the ciphers that the client is permitted to negotiate. If the setting is left empty, the Airlock Gateway default will be used. Restrictions:
|
Force new session | Checkbox to enable/disable forced restart of SSL/TLS handshake. |
Section Server Certificate Validation | |
ON/OFF | Enables or disables the server certificate validation mechanism. |
Verify hostname | Checkbox to disable/enable hostname verification. Default is enabled. Hostname verification requires a server identity check in combination with a valid CA chain to mitigate man-in-the-middle attacks. Without a CA, the configuration validation will fail. See also CAs for server chain validation. |
CAs for server chain validation | Certificate chain verification to make sure a given certificate chain is valid, properly signed, and trustworthy. A CA has to be added when Verify hostname is enabled, otherwise, the configuration validation will fail. |
Content of CAs for server chain validation | Shows the chain of trust of the certificate chain. |
Further information and links
- JWKS providers configuration
- JWKS providers for a mapping can be selected here: Section – Access Tokens
- The filtering/selection of JWKS and individual keys is described here: JWKS and JWK selection
- Back-end groups SSL settings